Research:
What are structural Isomers?
Online definition: In chemistry isomerization is the process by which one molecule is transformed into another molecule which has exactly the same atoms, but the atoms have a different arrangement
My definition: When the arrangement of a molecule is changed but still has all of the same atoms. (Alkanes)
Examples:
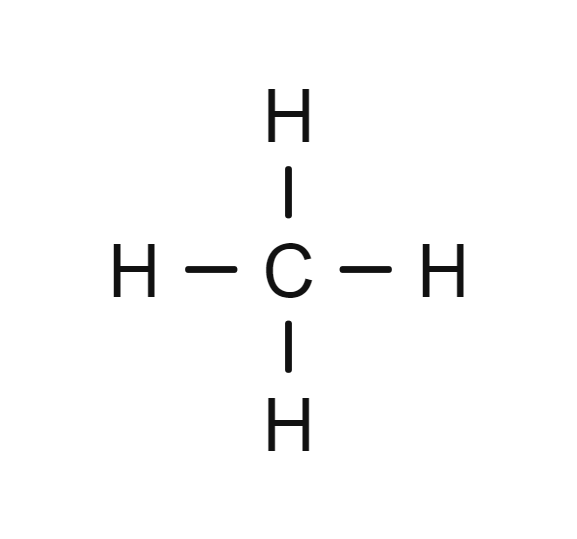
- Methane
- Ethane
- Propane
- Butane
VIDEO:
What are structural Isomers?
Online definition: In chemistry isomerization is the process by which one molecule is transformed into another molecule which has exactly the same atoms, but the atoms have a different arrangement
My definition: When the arrangement of a molecule is changed but still has all of the same atoms. (Alkanes)
Examples:
- Methane
- Ethane
- Propane
- Butane
VIDEO:
Constitutional Isomers: Isomers that differ in connectivity
Simple hydrocarbons such as; methane, ethane, and propane can not have constitutional isomers because there is no other way to connect them.
There are 2 different butanes that re constitutional isomers.
CITATIONS:
“What Is Isomerization? - Definition from Petropedia.” Petropedia.com, www.petropedia.com/definition/7019/isomerization.
“Isomerization.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 23 Sept. 2018, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Isomerization.
Jones, Maitland. “Isomerism.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 18 Oct. 2016, www.britannica.com/science/isomerism.



Comments
Post a Comment